
With these test conditions, analysis of measured bremsstrahlung radiation in various thicknesses and configurations of lead and plastic shielding shows the following: placing plastic first vs. With the source ( 32P) and detector held at a constant separation distance, we inserted lead and/or plastic absorbers and measured the reduction in bremsstrahlung radiation level measured by the detector. Using 32P beta radiation, we measured bremsstrahlung photons transmitted through lead and plastic (Lucite) shielding in different test configurations to determine the relative efficacy of lead alone, plastic alone, and the positional order of lead and plastic. This advice is based on the well established theory that radiative losses (bremsstrahlung production) are more prevalent in higher atomic number ( Z) materials than in low Z materials. Radiation protection literature is ubiquitous in advising the placement of plastic first to absorb all the beta particles before any lead shielding is used. Through this we hope to clarify a topic that is often confusing and concerning for many.Lead and plastic are commonly used to shield beta radiation.

What is the wavelength and frequency of this radiation? At each significant point along the way we will stop and consider: The shape of this energy curve depends on what fraction of the reaction energy (Q value-the. Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain fission.

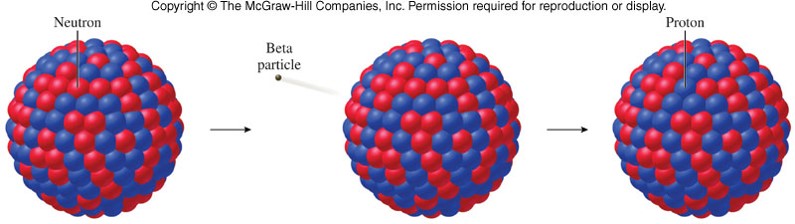
Ejected from the nucleus during beta decay, a beta particle is a fast moving electron. In this course, we will travel along the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation from unimaginably long to infinitesimally small wavelengths. What is Beta Particle Definition Description Beta Particles. Beta particles are either electrons or positrons ejected from the nucleus. Yet few people really understand what X-rays are or where they come from. Most of us have had an X-ray at some point in our life, at the Dentist, in a hospital or clinic. X-ray radiation, for example, is a scientific and medical discovery that has improved or prolonged billions of lives. This MOOC will allow the world to see radiation in a new light, to expose its benefits as well as its risks. Because a beta particle has a much smaller mass. Yet the word has become synonymous with danger, death and disaster. Just like alpha particles, beta particles interact electro- mechanically with orbital electrons (see 1.2.e). If the unstable atomic nucleus has an excess of the proton, then a positron (+) is emitted during decay.
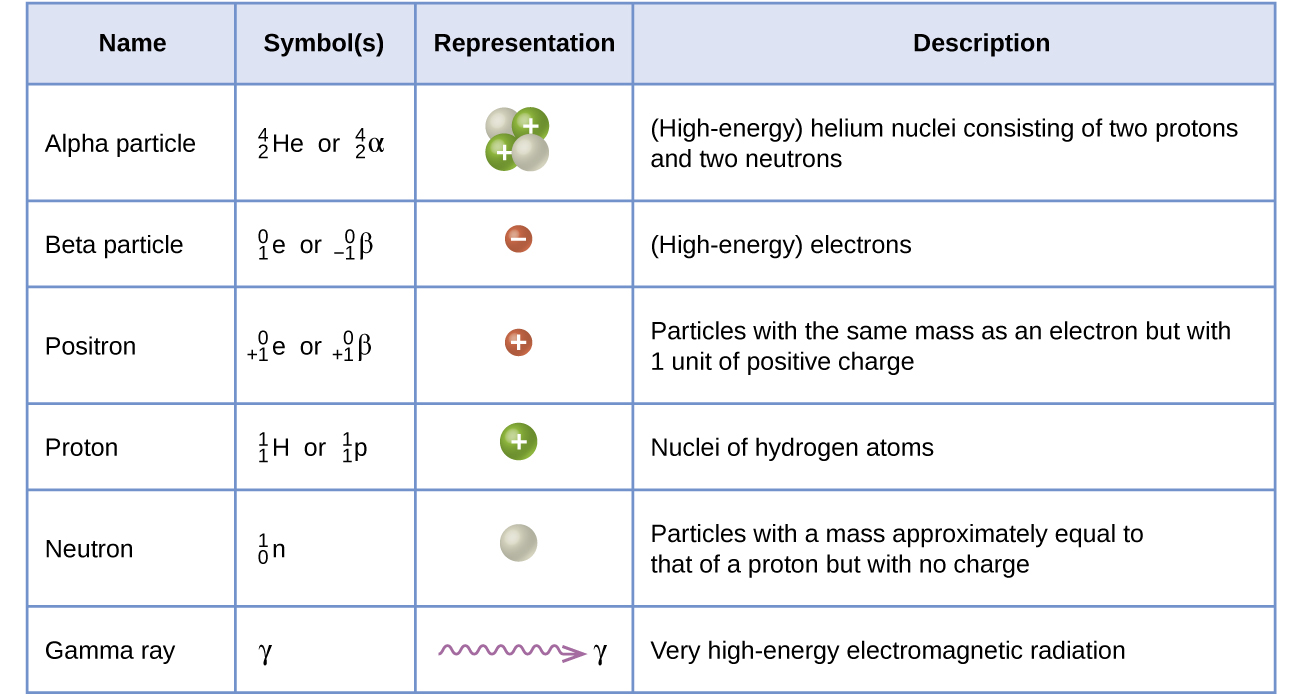
An unstable atomic nucleus with an excess of neutrons will emit electrons (-) during the decay. A high-speed electron or positron, usually emitted by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. Radiation is all around us - without it we wouldn’t exist. Beta particles, also known as beta rays, are a high speed, high energy electron (-) or positron (+) emitted from the radioactive decay of the atomic nucleus. Scientific definitions for beta particle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
